What is Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)?
Learn what Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is and how it helps teams manage product data, processes, and collaboration across the lifecycle. Discover the key benefits and PLM tools driving innovation.

A simulation is an imitation of a real system or process. Simulation is used to understand, predict, or analyse how a system behaves under different conditions. To do a simulation, you need to use computational techniques to solve the underlying mathematical models. In the manufacturing industry, simulation is used to test, analyse, and optimise products and processes before physical prototypes are built or production begins.

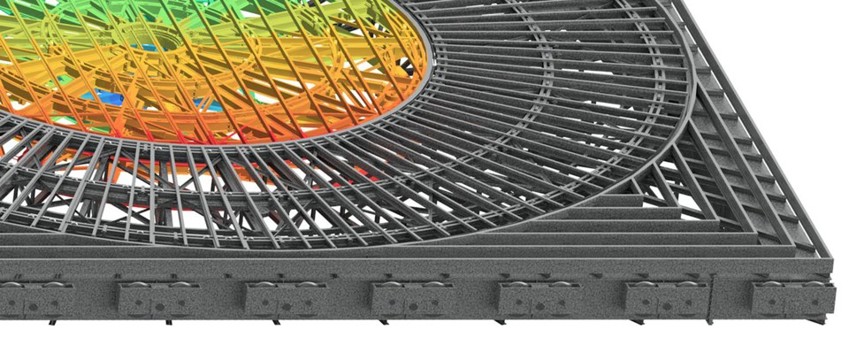
The Finite Element Method (FEM) is a common computational method used in simulation where a geometric area is divided into small elements and for each element the solution is approximated by functions. All elements are connected to a system of equations that are solved numerically. FEM is used in Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to simulate material stresses, deformations, heat flow and temperature distribution in products.
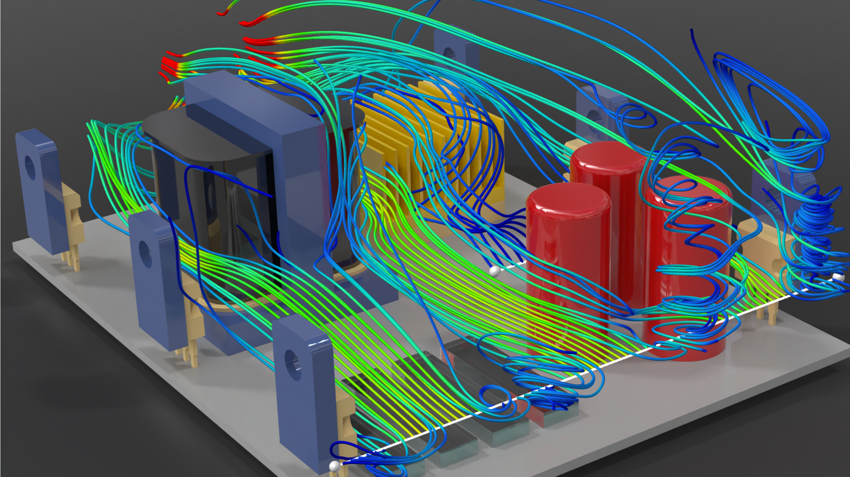
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a common computational method in fluid mechanics that solves the Navier-Stokes equations. The flow domain is divided into control volumes, and flow parameters are calculated in each cell. In simulation, CFD is used to optimise airflow, cooling, and pressure distribution.
Using simulation early in the product development process means you can:
There are several powerful simulation tools on the market. Symetri offers, for example:
Simulation has become an indispensable part of the manufacturing industry. By using advanced manufacturing solutions in simulation, such as FEA and CFD, companies can reduce costs, improve product quality, and accelerate the development process.
Want to learn more about how your organisation can benefit from simulation? Contact us at Symetri for a customised solution.
Learn what Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is and how it helps teams manage product data, processes, and collaboration across the lifecycle. Discover the key benefits and PLM tools driving innovation.
Discover what ISO 19650 is, how it supports BIM information management, and why it’s essential for digital construction. Learn how Symetri Ireland can help your team implement ISO 19650 workflows.
Learn what design means and how different types of design are used in the construction industry. Streamline your project with Symetri's digital solutions.
